티스토리 뷰
Cascade R-CNN: High Quality Object Detection and Instance Segmentation
Arc Lab. 2019. 8. 23. 14:29[업데이트 2019.08.24 12:22]
1. 논문
Cascade R-CNN: High Quality Object Detection and Instance Segmentation
arXiv:1906.09756v1 [cs.CV] 24 Jun 2019
2. 요약
Index Terms—Object Detection, High Quality, Cascade, Bounding Box Regression, Instance Segmentation.
- A multi-stage object detection architecture, the Cascade R-CNN, composed of a sequence of detectors trained with increasing IoU thresholds
- The observations above suggest that high quality detection requires a close match between the quality of the detector and that of the detection hypotheses.
- training a detector with higher threshold leads to poorer performance, as the paradox of high-quality detection.
- First, object proposal mechanisms tend to produce hypotheses distributions heavily imbalanced towards low quality. In result, the use of larger IoU thresholds during training exponentially reduces the number of positive training examples. This is particularly problematic for neural networks, which are very example intensive, making the “high u” training strategy very prone to overfitting.
- Second, there is a mismatch between the quality of the detector and that of the hypotheses available at inference time. Since, as shown in Fig. 2, high quality detectors are only optimal for high quality hypotheses, detection performance can degrade substantially for hypotheses of lower quality.
- In this paper, we propose a new detector architecture, denoted as Cascade R-CNN, that addresses these problems, to enable high quality object detection.
- The new architecture is a multi-stage extension of the R-CNN, where detector stages deeper into the cascade are sequentially more selective against close false positives.
- the cascade of R-CNN stages is trained sequentially, using the output of one stage to train the next.
- This leverages the observation that the output IoU of a bounding box regressor is almost always better than its input IoU, as can be seen in Fig. 2 (a), where nearly all plots are above the gray line. In result, the output of a detector trained with a certain IoU threshold is a good hypothesis distribution to train the detector of the next higher IoU threshold. This has some similarity to boostrapping methods commonly used to assemble datasets for object detection
- The main difference is that the resampling performed by the Cascade R-CNN does not aim to mine hard negatives. Instead, by adjusting bounding boxes, each stage aims to find a good set of close false positives for training the next stage
- In result, the sequence of detectors addresses the two problems underlying the paradox of highquality detection.
First, because the resampling operation guarantees the availability of a large number of examples for the training of all detectors in the sequence, it is possible to train detectors of high IoU without overfitting.
Second, the use of the same cascade procedure at inference time produces a set of hypotheses of progressively higher quality, well matched to the increasing quality of the detector stages. This enables higher detection accuracies, as suggested by Fig. 2.





- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- English
- SSM
- Jekyll and Hyde
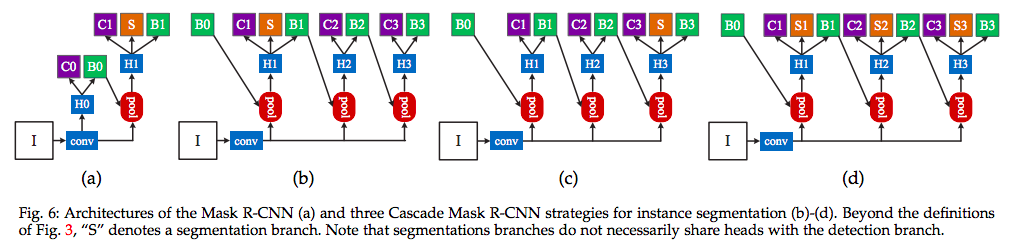
- Mask R-CNN
- belief
- some time ago
- Ragdoll
- 2D Game
- GOD
- aws #cloudfront
- #TensorFlow
- #ApacheZeppelin
- #ELK Stack
- project
- Physical Simulation
- #ApacheSpark
- #REST API
- sentence test
- Memorize
- OST
- Sea Bottom
- ILoop Engine
- 도커
- Game Engine
- docker
- Library
- Badge
- ate
- Meow
- Worry
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
